The most effective ways to remove stains from teeth instantly
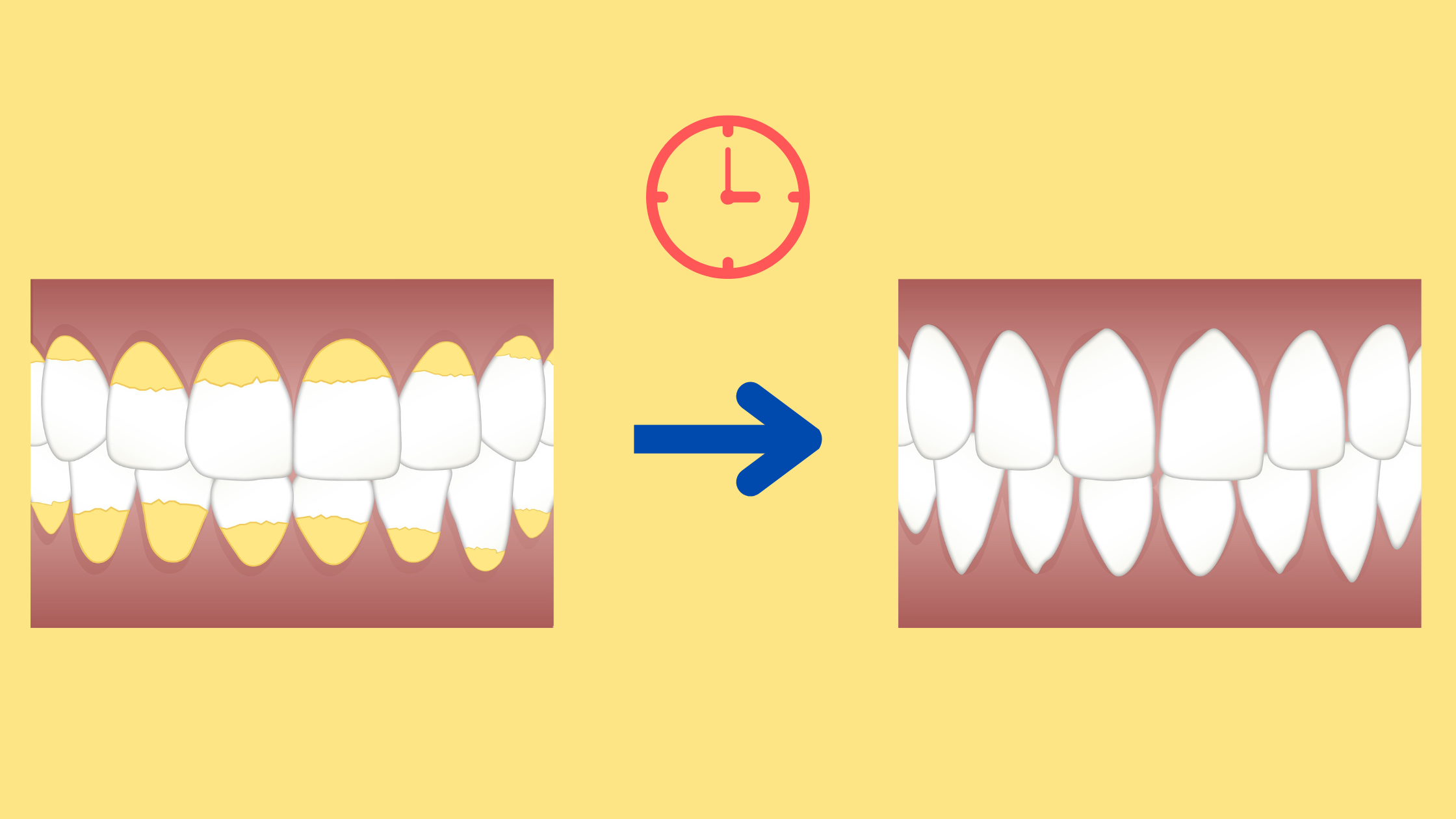 If you're a coffee lover or sometimes forget to brush your teeth, it’s no surprise if you wake up one day with black or brown stains on your teeth.
If you're a coffee lover or sometimes forget to brush your teeth, it’s no surprise if you wake up one day with black or brown stains on your teeth.
But don’t worry—you’re not alone. Tooth discoloration is a common issue for many people. The good news? There are plenty of solutions to help you achieve a brighter, more confident smile.
Some methods can deliver fast, even instant, results. However, the effectiveness depends on several factors, including the cause of the stain, the technique used, and the concentration of the whitening agents.
So, before starting any treatment, it’s crucial to identify the type of stain and its cause to find the best solution for your teeth.
Keep reading to discover what causes tooth discoloration and the most effective treatments to remove these stains quickly and permanently.

The Fastest Ways to Remove Tooth Stains (Sometimes Instantly)
1. In-Office Whitening

We’ve placed this at the top of the list because it’s the only option that almost always delivers instant results, often from the very first appointment. That's because the dentist uses high concentrations of bleaching agents, making it the ideal choice if you have severe discoloration or need quick results.
Jump to details
2. At-Home Tray-Based Teeth Whitening

If you prefer treating your teeth at home, this is the second option you should consider. We’ve ranked it second because it's the best at-home option that keeps the whitening gel in close contact with your teeth, whitens them evenly on all sides, and delivers results similar to a professional treatment.
Jump to details
3. Whitening Strips

If at-home whitening trays aren’t your thing, whitening strips are a great alternative. They’re less expensive and can still give you the results you want. The downside? They might miss some spots on the sides of your teeth. But they’re still a solid option if you’re dealing with mild to moderate discoloration.
Jump to details
4. Paint-On Gels

We’ve placed this at the bottom of the list because, while it can deliver fast, sometimes instant results, it’s not a long-term solution. Think of it as tooth makeup—you’ll need to reapply it regularly to maintain the look. This product works mostly through an optical effect, creating a thin layer on your teeth that only lasts a short time.
Jump to details
How Fast Whitening Treatments Work: Evidence-Based Comparison
| Study | Results |
|---|---|
| At-Home Vs. In-Office Whitening (1) |
|
| OTC Vs. In-Office Vs. At-Home Whitening (2) |
|
| 6% Whitening Strips Vs. Two Whitening Toothpastes (3) |
|
1. How do stains appear on our teeth?
2. The Key Things About Whitening Products
3. The Most Effective and Quick Ways to Whiten Teeth
4. Other Teeth Whitening Solutions
5. What You Should Know Before Starting Any Whitening Treatment
6. Alternatives to Teeth Whitening
How do stains appear on our teeth?
Tooth discoloration can have different causes and factors. These can broadly be divided into two types: extrinsic and intrinsic stains.1. Extrinsic Tooth Stains:
Extrinsic stains appear on the surface of the teeth (limited to the enamel) and are caused by external factors. Here are some common causes of extrinsic tooth stains:
- Plaque and Tartar: Plaque buildup on teeth can cause yellow or brown stains. If left untreated, plaque can harden into tartar, which is even harder to remove.
- Smoking: Tobacco use can cause dark brown or yellow stains on teeth.
- Certain foods: Certain foods and beverages, such as coffee, tea, red wine, and soda, can also stain our teeth over time due to a substance called tannins.
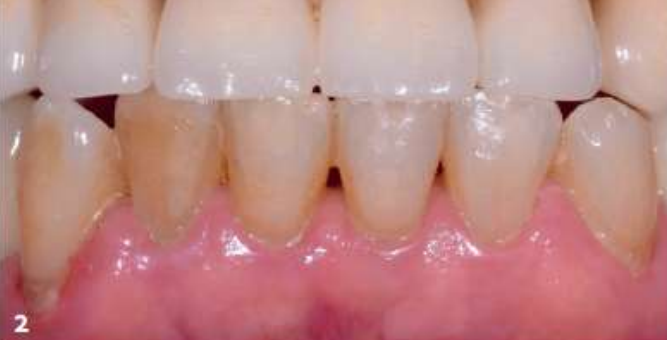
Extrinsic stains due to pigmented foods
Extrinsic stains are limited to the enamel surface. This is because enamel is naturally porous and can absorb pigmented substances.The good thing about extrinsic stains is that they're easier to remove with oral hygiene measures, at-home whitening techniques, and regular dental cleanings.
2. Intrinsic Tooth Stains:
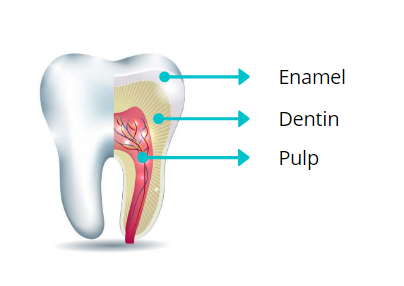
Intrinsic stains occur in the deep structures of the tooth, beyond the enamel. They are caused by internal factors. Here are some common causes of intrinsic tooth stains:
- Fluorosis: Children who have been exposed to high doses of fluoride while their teeth were developing can cause white or brown spots or lines on their adult teeth.
- Medication: Certain medications, such as tetracycline, can cause deep gray or brown stains on teeth.
- Trauma: A blow to the mouth or teeth can damage the nerves and blood vessels in teeth, leading to discoloration.
- Hypomineralization: This is a condition where the enamel has not developed properly, making the teeth appear discolored or chalky.
- Aging: As we age, the enamel on our teeth naturally thins, making the underlying dentin more visible. Dentin is naturally yellow, so as it becomes more visible, teeth can appear darker and duller.
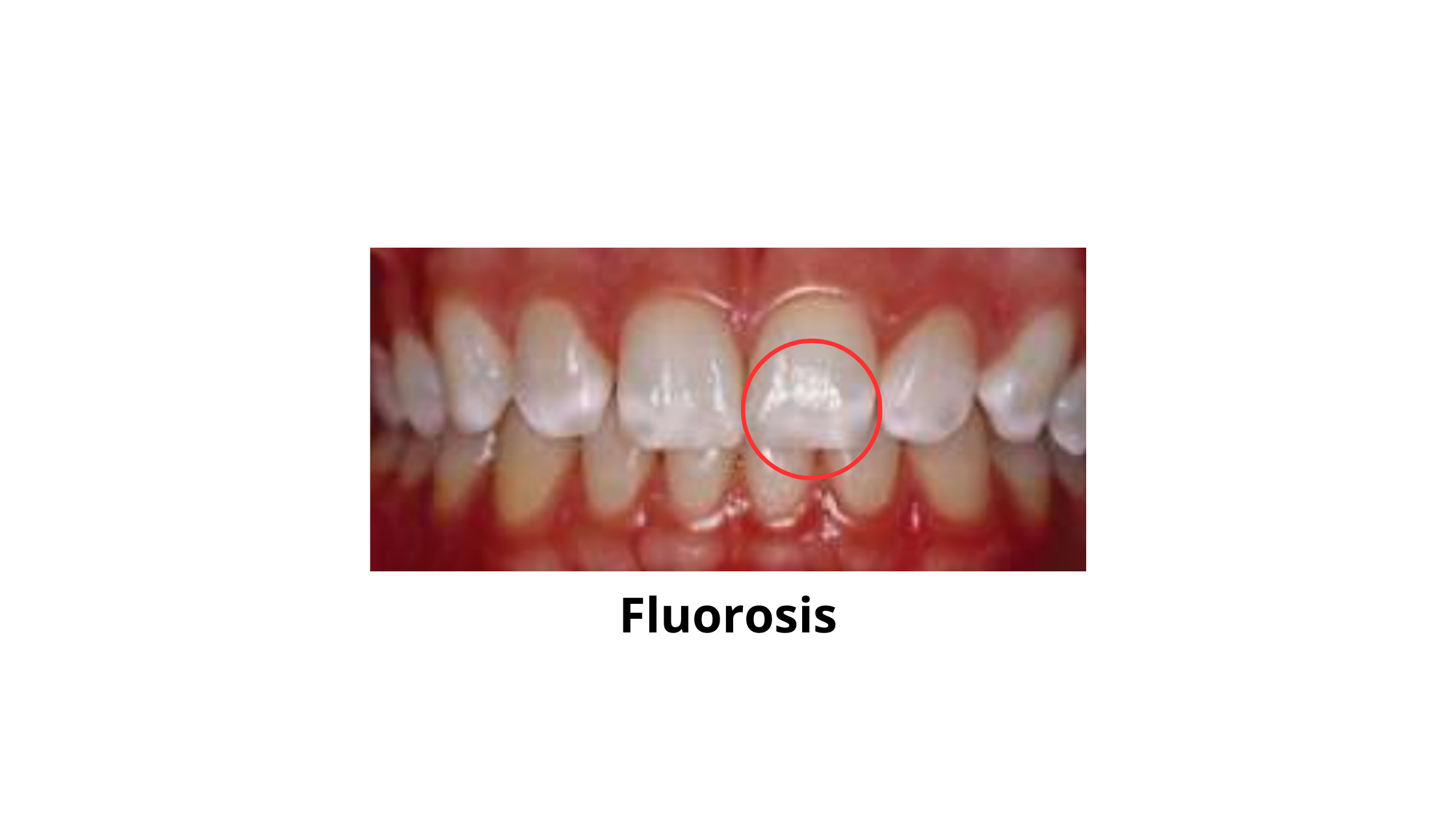 Intrinsic stains are harder to remove because they affect the deep structures of the tooth, including the dentin. Treatment for intrinsic stains may involve more advanced cosmetic dentistry procedures, such as professional teeth whitening or veneers.
Intrinsic stains are harder to remove because they affect the deep structures of the tooth, including the dentin. Treatment for intrinsic stains may involve more advanced cosmetic dentistry procedures, such as professional teeth whitening or veneers.
Now that we've covered the different factors that can cause stains on teeth, let's explore how whitening treatments work and the most effective techniques.
The Key Things About Whitening Products
All effective whitening methods work in the same way: the active ingredients penetrate deep into the tooth's enamel and dentin, breaking down the chemicals that cause stains.The most common bleaching agents are hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide.
However, it’s hydrogen peroxide that does the job. For example, a 10% concentration of carbamide peroxide whitens teeth by releasing around 3% hydrogen peroxide.
So, a product with 6% hydrogen peroxide is actually stronger than one with 15% carbamide peroxide.
Overall, here are some key important things to remember about these whitening agents:
- Concentration: The higher the concentration of the peroxide agent, the faster and more noticeable the whitening results.
- Sensitivity risk: Higher concentrations also come with a higher risk of sensitivity and side effects.
- Peroxide needs time to work its magic: For the active ingredients to work effectively, they need to be left on the tooth surface for a specific period, as directed.
- Proper storage: Peroxide-based whitening products should be stored in a cool, dark environment. Storing them in the refrigerator can help extend their shelf life. Otherwise, they may no longer be effective.
The Most Effective and Quick Ways to Remove Stains from Teeth
Removing those surface stains is pretty straightforward. You can do this by just improving your regular oral hygiene routine and brushing your teeth thoroughly with the right technique.But what if you want faster results? That’s when some whitening methods can help.
1. In-Office Whitening:
If you're looking for an immediate solution to remove stubborn deep and severe stains, in-office whitening is the best option. It often provides instant results.
During the procedure, your dentist will apply a highly concentrated whitening gel containing 15-38% hydrogen peroxide or up to 35% carbamide peroxide. The application may be repeated 3 to 4 times within the same session, with each application lasting 10 to 20 minutes. On average, the entire session typically lasts between 30 to 90 minutes.
While superficial stains usually vanish immediately, it's important to wait for 24 hours after the treatment to allow the color of your teeth to stabilize.
That’s because after the treatment, your teeth become dehydrated, which can make them look whiter than they actually are.
Pros:
- Immediate and noticeable whitening effects.
- Safe.
Cons:
- The most expensive whitening option.
- Risk of potential side effects, such as tooth sensitivity or gum irritation, due to the high concentration of bleaching agents.
2. At-Home Whitening Treatment
1. At-Home Tray-Based Teeth Whitening
If in-office whitening isn’t an option, home tray-based whitening treatment is a great alternative. It’s safe, budget-friendly, and can deliver results similar to professional treatments—all from the comfort of your home.
These kits usually include a gel, primarily made of carbamide peroxide, along with a tray or mouth guard. Some trays come with built-in LED lights that help speed up the whitening process.
Simply apply the whitening gel to the mouthpiece and wear it for the recommended time, which can range from 30 minutes to a few hours per day.
The peroxide concentration is lower than what dentists use, making it safer and gentler for at-home use.
Studies have shown that teeth whitening trays can achieve results comparable to in-office whitening, though it may take a bit longer.
One study compared a one-hour in-office whitening session using 25% hydrogen peroxide with a 5-day overnight tray-based treatment using 10% carbamide peroxide—and found that the results were similar.
Pros of Teeth Whitening Trays
Cons of Teeth Whitening Trays
Easy to use
Takes longer than in-office whitening
More affordable than in-office treatment
Comparable results to in-office whitening
2. Whitening Strips
When used properly as directed, whitening strips can deliver excellent and long-lasting results, similar to other options.
Strips are perfect if your stains aren’t too bad and tray whitening isn’t an option. The active ingredient is usually hydrogen peroxide 5% up to 14%.
They're easy to use: just apply the gel side of the strip to the front side of your teeth. How often and how long you should use them depends on the specific product and its hydrogen peroxide concentration. Simply follow the instructions on the label.
Typically, it takes about 1 to 2 weeks to notice improvements.
A study found that both whitening strips (with 5% hydrogen peroxide) and in-office whitening (with 38% hydrogen peroxide) were effective. While in-office whitening achieved results in a single session, whitening strips required about two weeks to achieve similar results.
Pros of Whitening Strips
Cons of Whitening Strips
Convenient and easy to use at home
It may take longer to notice results
Can provide great and long-lasting results
They may miss certain areas on the teeth
More affordable compared to in-office treatments
Some individuals may experience mild gum irritation or tooth sensitivity
Minimal sensitivity compared to higher-concentration whitening methods
3. Paint-On Gels
Paint-on gels have recently become a popular trend for at-home teeth whitening. They come in a pen-like applicator filled with a bleaching agent, often peroxide-based.
They’re affordable and can be effective for minor stains that aren’t too deep.
Using them is straightforward: simply twist or press the tip of the pen to release the gel, apply it evenly to the front of your teeth, and let it dry. Once dry, you’re ready to go.
However, they’re not the best option for long-term results. Paint-on gels mainly work by creating a visual effect—temporarily brightening your teeth with a thin white layer. Once that layer wears off, the whiteness fades.
To keep the effect, you’ll need to reapply the gel regularly.
They can be a suitable option for quickly brightening your teeth before a special occasion, like a meeting, date, or social event.
Pros of Paint-On Gels
Cons of Paint-On Gels
Simple and easy-to-use
Temporary results that fade as the gel wears off
Provides a quick fix for minor staining
Limited effectiveness for severe discoloration
Affordable compared to other whitening methods
May not provide long-lasting whitening effects
Portable and convenient for on-the-go touch-ups
In-office whitening treatments can provide instant and noticeable results in just one session.
At-home whitening methods, while needing consistent use, can achieve similar results over time.
Other Teeth Whitening Solutions
Peroxide-based whitening treatments use chemicals to brighten teeth and are the most effective for deep or stubborn stains.
Other options like whitening toothpastes, toothbrushes, and chewing gums mainly work by mechanically removing surface stains through gentle abrasion.
While some toothpastes and mouthwashes claim to contain peroxide whitening agents, their concentration is usually too low to make a noticeable difference.
1. Whitening Toothpastes:
Most whitening toothpastes contain abrasive agents that help scrub away surface stains. Common abrasives include silica, baking soda, and calcium carbonate.
Because these toothpastes are abrasive, it’s important not to overuse them or brush too hard. Using them too often or applying too much pressure can damage your teeth and gums, potentially causing sensitivity, gum recession, or even cavities.
For best results, use whitening toothpaste for up to three weeks at a time, or alternate it with a gentler toothpaste to protect your teeth and gums.
2. Practice Good Oral Hygiene
Improving your oral hygiene may be all you need to remove minor surface stains. Here are some helpful tips:
- Use an Electric Toothbrush: An electric toothbrush can provide a more thorough cleaning compared to a manual one. Its rotating or vibrating action helps remove plaque and stains more effectively.
- Brush Properly with a Manual Toothbrush: If you prefer a manual toothbrush, make sure you’re brushing correctly. Use gentle, circular motions to clean all surfaces of your teeth, including the front, back, and chewing surfaces. Don’t forget to brush your tongue, as bacteria can accumulate there too.
- Clean Between Your Teeth: Brushing alone doesn’t reach all areas of your mouth. Use dental floss or interdental brushes to clean between your teeth where plaque and food particles can get trapped.
3. Sugar-Free Chewing Gums
Sugar-free chewing gums don’t whiten teeth directly, but they can help prevent stains and reduce plaque buildup. Choose gums that contain tooth-friendly ingredients like xylitol and sodium hexametaphosphate.
- Xylitol has anti-plaque properties and helps inhibit the growth of bacteria that cause cavities.
- Sodium hexametaphosphate helps reduce stains by changing how discoloring substances stick to your teeth.
What You Should Know Before Starting Any Whitening Treatment
Teeth whitening is generally a gentler way to brighten your smile compared to other dental procedures, but it’s not suitable for everyone. For some individuals, peroxide-based treatments might cause more harm than good. Here’s when you should be cautious:
- Cavities or fractures: Address any untreated cavities or fractures in your teeth before starting whitening treatment.
- Gum disease: If you have active gum disease or gum recession, whitening treatments may increase sensitivity.
- Sensitivity issues: For those with existing tooth sensitivity, whitening treatments might worsen the problem. Consult your dentist for alternative or gentler options.
- Young patients: Whitening treatments are usually not recommended for individuals under 15 years old, as their teeth are still developing and porous.
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women: Whitening agents could potentially affect the developing fetus or nursing baby.
- Smokers: Hydrogen peroxide may interact with tobacco, which can increase the toxic effects of smoking and limit whitening results.
- Allergy to whitening ingredients: Some people may be allergic or sensitive to ingredients in whitening products.
Higher concentrations of whitening agents also come with increased risks of side effects:
- Effects on enamel and dentin: Stronger whitening agents can temporarily weaken enamel or increase tooth sensitivity, though these effects are usually reversible.
- Effects on soft tissues: Whitening agents might irritate the soft tissues of the mouth, causing sores, burns, or whitish discoloration.
Tips to Manage Side Effects:
- Apply a desensitizing gel or toothpaste to your teeth before starting the whitening treatment. Leave it on for a few minutes before brushing, for 7 days.
- Continue using the desensitizing product for the first two weeks after whitening.
- Strengthen your enamel and restore its hardness by using a fluoride supplement or remineralizing agent, such as mouthwash, foam, or dental gel.
Alternatives to Teeth Whitening
For individuals who may not be suitable candidates for teeth whitening, there are alternative options available to restore their smile and improve the appearance of their teeth. These alternatives include:
1. Microabrasion
This gentle technique can deliver immediate results if the stains are limited to the enamel layer. It involves removing a thin layer of enamel—where the stains are trapped—using acid etching combined with an abrasive agent.
2. Icon resin infiltration
This is an ideal option if you have white spot lesions caused by fluorosis or early decay. The technique is done in a single visit and involves filling the tiny pores of the white spots with a fluid resin dental material.
3. Veneers
Veneers are thin shells that are bonded to the front of your teeth to cover imperfections like stains, chips, or gaps.
They’re usually made from a highly aesthetic material called porcelain. Since they’re custom-made and match the color of your natural teeth, the results are often excellent and very natural-looking.
-
Comparison of at-home and in-office tooth whitening using a novel shade guide - PubMed (nih.gov)
-
Efficacy, side-effects and patients' acceptance of different bleaching techniques (OTC, in-office, at-home) - PubMed (nih.gov)
-
Clinical trial of tooth whitening with 6% hydrogen peroxide whitening strips and two whitening dentifrices - PubMed (nih.gov)
-
opinion on hydrogen peroxide (europa.eu)
-
For the all important winning smile | British Dental Journal (nature.com)
| Pros of Teeth Whitening Trays | Cons of Teeth Whitening Trays |
|---|---|
| Easy to use | Takes longer than in-office whitening |
| More affordable than in-office treatment | |
| Comparable results to in-office whitening |
| Pros of Whitening Strips | Cons of Whitening Strips |
|---|---|
| Convenient and easy to use at home | It may take longer to notice results |
| Can provide great and long-lasting results | They may miss certain areas on the teeth |
| More affordable compared to in-office treatments | Some individuals may experience mild gum irritation or tooth sensitivity |
| Minimal sensitivity compared to higher-concentration whitening methods |
| Pros of Paint-On Gels | Cons of Paint-On Gels |
|---|---|
| Simple and easy-to-use | Temporary results that fade as the gel wears off |
| Provides a quick fix for minor staining | Limited effectiveness for severe discoloration |
| Affordable compared to other whitening methods | May not provide long-lasting whitening effects |
| Portable and convenient for on-the-go touch-ups |
At-home whitening methods, while needing consistent use, can achieve similar results over time.
Tips to Manage Side Effects:
- Apply a desensitizing gel or toothpaste to your teeth before starting the whitening treatment. Leave it on for a few minutes before brushing, for 7 days.
- Continue using the desensitizing product for the first two weeks after whitening.
- Strengthen your enamel and restore its hardness by using a fluoride supplement or remineralizing agent, such as mouthwash, foam, or dental gel.
- Comparison of at-home and in-office tooth whitening using a novel shade guide - PubMed (nih.gov)
- Efficacy, side-effects and patients' acceptance of different bleaching techniques (OTC, in-office, at-home) - PubMed (nih.gov)
- Clinical trial of tooth whitening with 6% hydrogen peroxide whitening strips and two whitening dentifrices - PubMed (nih.gov)
- opinion on hydrogen peroxide (europa.eu)
- For the all important winning smile | British Dental Journal (nature.com)