Why do I have a bump on my mouth inside the cheek? (pictures)
 If you've recently noticed a bump on the inside of your cheek, you might be wondering what it is and what you should do about it.
If you've recently noticed a bump on the inside of your cheek, you might be wondering what it is and what you should do about it.
In this article, we'll provide you with the information you need to know exactly what this bump is, and give you guidance on the steps to take.
Please keep in mind that while most bumps in the mouth are harmless, it's always a good idea to see a dentist or healthcare professional if you notice one. Only they can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend the most appropriate treatment plan for you.
In this article...
1. What can a bump on the mouth, inside the cheek mean?
2. Why are bumps more likely to form on the inside of cheeks?
3. When to Worry About a Bump
4. Aggravating factors
5. How to deal with a bump in the mouth?
What can a bump on the mouth, inside the cheek mean?
If you notice a bump on the inside of your cheek, there's no need to overthink it. Most of them are benign and nothing to worry about.While certain symptoms can give you an idea, the only way to know for sure is through a biopsy and lab test, as many harmless growths can look alike.
Here are some of the most common causes:
1. You have a single non-painful bump on your cheek (fibroma)
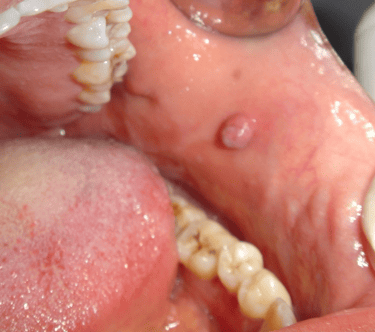
This type of lump is fairly common in the mouth and usually develops due to constant, long-term irritation from things like repeatedly biting your cheeks or wearing an old, poorly fitting denture.
We call them fibrous overgrowth or fibroma because they result from a benign overgrowth of fibroblast cells, which start producing too much collagen protein.
They appear as a single mass, between 1 and 2 centimeters in size (roughly the size of a pea), which may be firm or soft to the touch. They can grow flat against the mouth lining or hang by a small stem.
Its surface is usually smooth and has the same color as the surrounding tissue, but it can sometimes be inflamed and turn white or red due to injury. Fibromas are not and never turn into cancer.
In rare cases, the lump may bleed easily when touched. When this happens, the growth is made up primarily of blood vessels and rapidly grows to about half an inch in size. These are primarily found in pregnant women because of hormonal changes.
2. You have a soft, blister-like lump (mucocele)
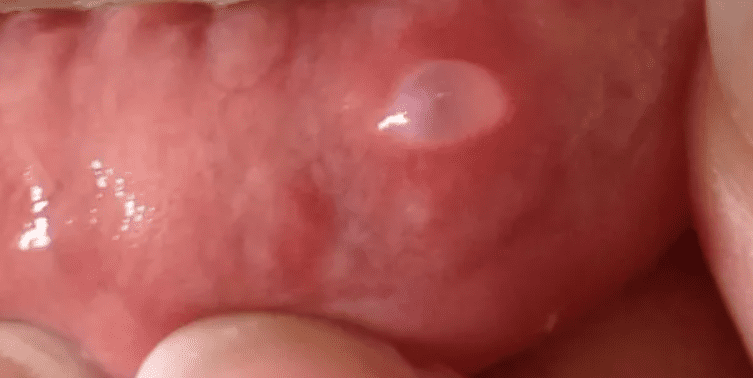
A soft, clear, or bluish lump anywhere in your mouth is usually a sign of a mucocele (also known as a mucoid cyst). Along with fibromas, they are one of the most common growths of the mouth (affecting around 2.4 out of every 1,000 people).
It doesn’t have the firm texture of a tumor. Instead, the cyst is softer, and when you touch it, you can feel that it’s filled with fluid.
It happens when the ducts of the salivary glands — which release saliva into your mouth — get injured. When this happens, saliva gets trapped in the inner layer of your mouth. This can lead to a swelling that may be painful and can range in size from a few millimeters to a few centimeters.
3. You have multiple blister-like lesions and painful ulcerations (viral infection)
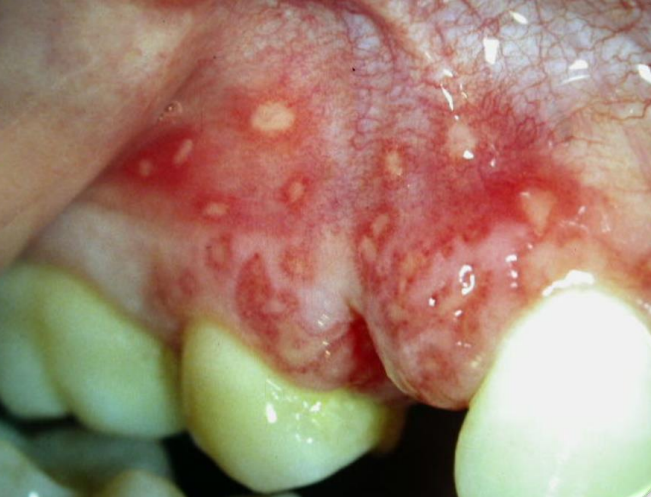
Having many painful, blister-like spots at once is usually a sign of a viral infection. This is most often caused by a herpes outbreak (commonly known as cold sores). But other viruses, like the varicella-zoster virus, can also cause many blisters to appear.
These can appear in different parts of the mouth, including the lips, inside of the cheeks, and gums. They soon break open to leave painful ulcers, which usually heal on their own within 10-14 days.
Other rarer conditions that can also cause blister-like lesions include erythema multiforme, mucous membrane pemphigoid and pemphigus. These are immune diseases that cause the body to mistakenly attack its own tissues.
4. You have a painless lump with a cauliflower-like surface (oral papilloma)
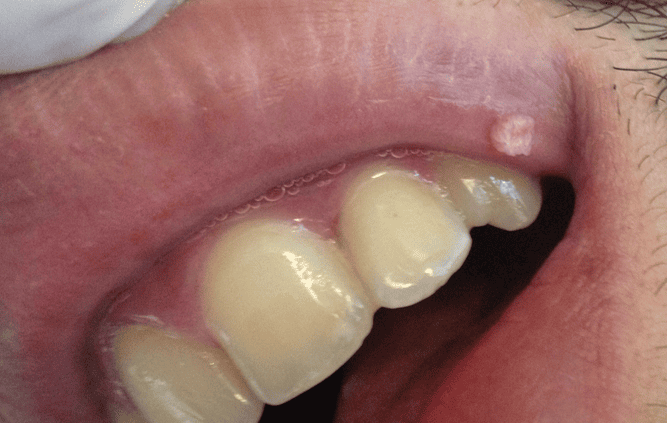
Oral papillomas, known as warts, are quite common and most often appear on the inside of the cheeks, tongue, gums, or lips. They are so-called because they are associated with the human papillomavirus (HPV) — a highly contagious virus that spreads through direct contact.
Oral papillomas usually show up as one or multiple small bumps on the lining of the mouth. They are typically painless and grow quickly, stopping once they reach about one centimetre in size.
Their surface is covered by a pink or white layer with grooves, giving them a cauliflower-like appearance.
5. Your cheek is swollen from the outside (benign salivary gland tumor)
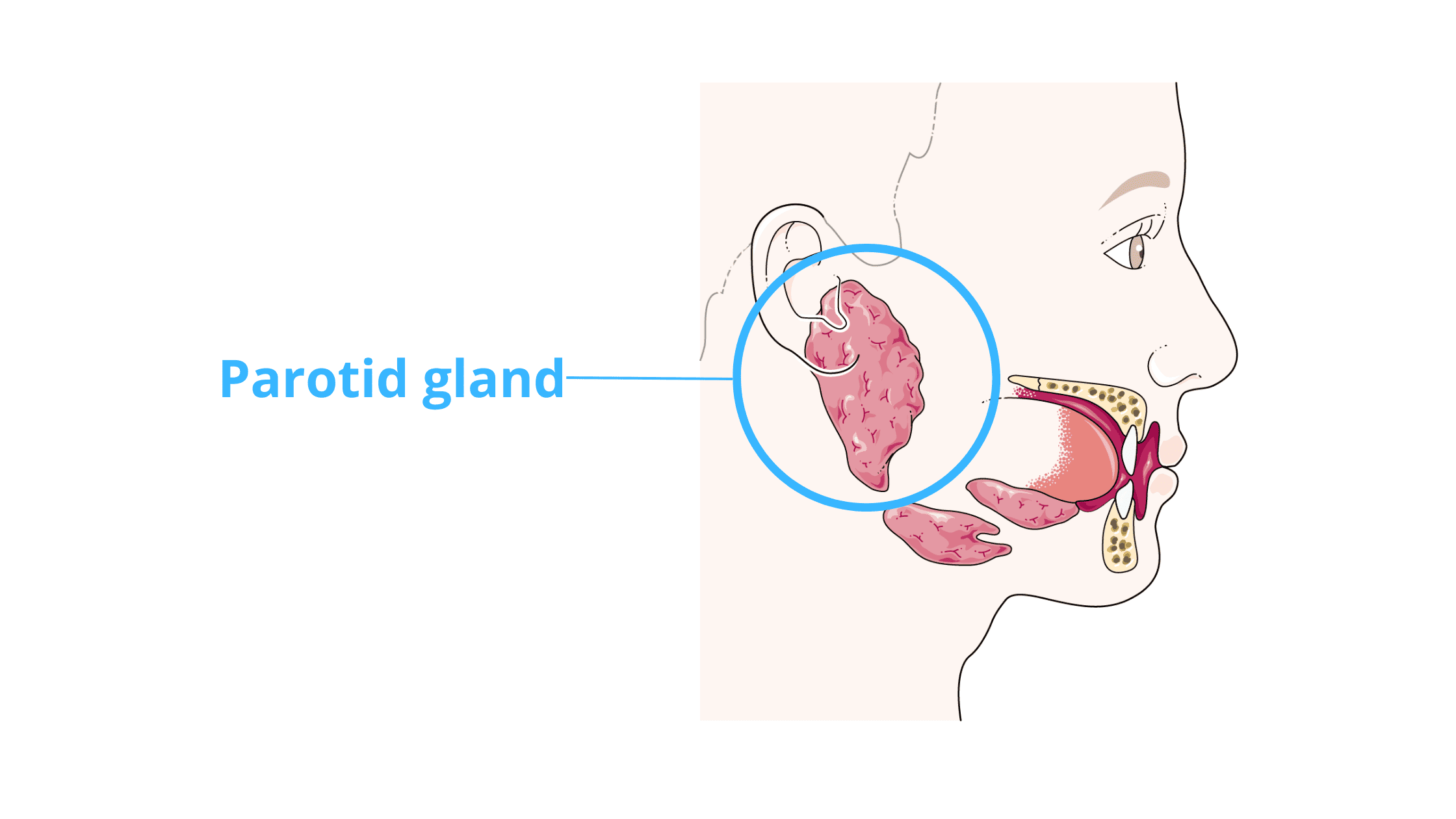
A firm swelling inside your cheek with a surface that looks normal and healthy, similar to the surrounding tissue, may indicate a benign salivary gland tumor. These are less common than other benign growths like fibromas or mucoceles.
The most common type is called Pleomorphic Adenoma. It usually feels like a firm lump, ranging in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters, and grows slowly without symptomps.
The parotid glands, located just in front of and below each ear, are the most commonly affected. If the tumor is in the parotid gland, swelling may also appear on the outside of the face.
However, salivary glands are found throughout the mouth, so any area can be affected.
Salivary gland tumors are mostly benign, and the risk of them becoming cancerous is quite low.
Why are bumps more likely to form on the inside of cheeks?
The inside of your cheek is lined with delicate tissue that's more susceptible to irritation and injury. Plus, this area of the cheek is right up against the teeth, making it more prone to repeated rubbing and biting.This can lead to the formation of sores, cysts, or bumps when the tissue reacts to the irritation.
The good news is that, aside from the discomfort they can cause when you eat, they are generally benign and pose no threat to your health. They usually stay where they first appear and grow slowly without spreading into surrounding tissues.
Can you tell exactly what the bump really is? Again, symptoms can give a good clue, but only a microscopic examination (biopsy) can reveal its true nature.
Many factors can make bumps in your mouth. The main reason is the constant irritation, but other things can be involved too, like:
- Infections.
- Trauma or injury.
- Rarely, malignant growth (oral cancer).
When to Worry About a Bump
While most lumps inside the mouth are harmless and don't have any cancerous potential, some oral lesions can be dangerous and carry a risk of becoming malignant.One common symptom to watch for is white patches in different areas of your mouth that can be either raised or flat. These may be a sign of a pre-cancerous condition called leukoplakia. It can appear anywhere in the mouth but is most common on the tongue, the inside of the cheeks, and the lower lip.
These white patches are firmly attached to the oral lining and cannot be wiped off.
Another sign to watch for is persistent red patches. These may indicate another pre-cancerous condition known as erythroplakia. This should be checked closely because it carries an even higher risk.
Other symptoms to watch out for include:
- The bump is growing or seems out of place: Benign growths usually grow slowly and stop once they reach a certain size. If the lump is growing quickly or keeps getting bigger, please have it checked as soon as possible.
- The boundaries look larger than they seem: Benign growths tend to stay in the area where they first appear and remain there for years. Cancerous growths, however, often have uneven or irregular edges and are more aggressive — they can invade and destroy surrounding tissues.
- Swollen lymph nodes: Swelling under your lower jaw or in your neck may be a sign that your lymph nodes are reacting to something. This is most often due to an infection, but it can sometimes indicate something more serious.
- Persistent pain: Benign lesions are usually painless unless they get injured. Oral cancer also rarely causes pain in its early stages, but if it grows larger and starts pressing on nearby nerves, it can cause a strange tingling or persistent pain.
- Unexplained bleeding: Chronic or unexplained bleeding in the mouth — whether from the gums, tongue, or any other area — should always be taken seriously and checked by a dentist.
Aggravating factors
Many factors can increase the risk of developing lumps or lesions in the mouth — and may even set the stage for cancerous changes. Combined with genetics, these factors can make some people more prone. These include:- Smoking: Tobacco contains hundreds of carcinogenic substances and toxins that can affect the oral mucosa and increase the risk of oral cancer. Smoking also increases mouth temperature, which can cause irritation.
- Alcohol: People who smoke and drink heavily at the same time are 35 times more likely to develop oral cancer than those who don't do both.
- Infections: Some viral infections, such as herpes virus, human papillomavirus and HIV, often show up on the oral mucosa as blisters, sores and bumps.
- Hormonal imbalance: Some hormonal conditions can affect the mouth resulting in red, swollen, and bleeding gums, swollen salivary glands, and canker sores.
- Chronic irritation: Repeated, long-term irritation of the mouth due to ill-fitting dentures, cheek bites or hot, spicy foods can injure oral tissues and lead to abnormal lesions.
- Nutritional deficiency: Deficiency of certain nutrients, particularly vitamins A, C and B-complex, and iron, has been associated with many oral conditions.
How to deal with a bump in the mouth?
Most mouth bumps or growths are benign, grow slowly, don’t damage surrounding tissue, and may not even require any treatment.However, some more serious (but rare) conditions can appear early as a bump, white or red patch, or ulcer.
To be safe, any change in your mouth — no matter how small it may seem — that doesn’t heal within 10 days should be checked by your dentist or a healthcare professional.
If the growth looks suspicious, it may need to be biopsied to find out exactly what it is.
Never try to remove or scrape a mouth lump at home, as this can make it worse or lead to an infection.
Once diagnosed, treatment usually involves surgical removal. It’s also important to address any risk factors, such as infections, smoking, or chronic irritation, to prevent the growth from coming back.
Sources
- What is oral (irritated) fibroma? https://dermnetnz.org/topics/oral-irritated-fibroma
- A Color Handbook of Oral Medicine - Richard C. K. Jordan, Michael A. O. Lewis
- Papillome buccal/Condylomeacuminé/Verrue vulgaire http://dermatologiebuccale-nice.fr
- “Parts of the figure were drawn by using pictures from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License”