Mouth breathing: Effects, Symptoms, Causes, Treatment Options, & More
 While occasionally breathing through the mouth is normal, chronic mouth breathing can lead to various health problems.
While occasionally breathing through the mouth is normal, chronic mouth breathing can lead to various health problems.
This habit usually starts in early childhood and becomes difficult to break later on. You may not even notice it, especially if you are used to breathing through your mouth at night.
The earlier the treatment, the easier it is and the more you will avoid the associated complications.
In this article, we'll explore the symptoms, causes, and effects of mouth breathing on your oral and general health. We will also discuss some treatment options that may help you make the switch to nasal breathing.
How do I know if I am a mouth breather?
Sometimes it's hard to tell on your own. This is especially true if you are used to it or if it happens at night, while you are sleeping. There are a few symptoms that may help you figure it out. The most common include:- Dry mouth and throat.
- Bad breath.
- Snoring or sleep apnea.
- Poor sleep and dark circles.
- Chronic fatigue.
- Repeated headaches.
- Poor concentration or focus.
- Dental problems such as cavities and gum disease.
- Swollen tonsils or adenoids.
- Changes in posture, facial structure and growth.
How is mouth breathing diagnosed?
Your doctor may perform several tests to confirm that you are suffering from chronic mouth breathing. Here are some of the methods used:- Visual test: Mouth breathers often have dark circles, an open mouth at rest, a long and straight face, and inflamed gums on the front teeth.
- Ask about your breathing habits: Your doctor will ask questions about when you first noticed your mouth breathing, how often it happens, the particular situations where it occurs most, and whether it is associated with other symptoms.
- Physical examination: Your healthcare provider will examine your nose, mouth, and throat for any anatomical abnormalities (enlarged tonsils or adenoids) that may be causing mouth breathing. They may also check your breathing in different positions.
- Diagnostic tests: The goal is to assess the function of your nose and airways. The simplest and best-known is the mirror test. Your physician will ask you to breathe out through your nose onto a mirror. Afterward, they will compare the airflow from both of your nostrils. If there's a noticeable discrepancy in size between the two, it might indicate an obstruction in your air passage.
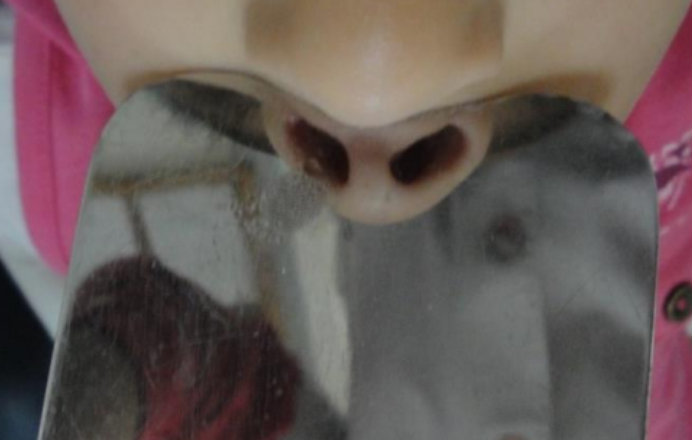
What can cause mouth breathing?
Again, occasional mouth breathing, such as when you exercise, is normal and should not be a concern. However, when it becomes a chronic habit, you need to find the cause to stop it.There are many possible causes of mouth breathing. Often there is a combination of many of them, which makes the treatment more complex.
In addition, the way your jaws, muscles, and posture adjust to this breathing pattern reinforces this negative habit, making it more challenging to break free from it.
The most common causes of mouth breathing are:
- Nasal obstruction: A blockage in the nasal airways, such as from allergies, congestion, or a deviated septum, can force a person to breathe through their mouth.
- Enlarged adenoids or tonsils: These structures at the back of the throat can become inflamed and enlarged, obstructing the airway and causing mouth breathing.
- Chronic sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinuses can cause nasal congestion and difficulty breathing through the nose.
- Habitual mouth breathing: Some people develop a habit of breathing through their mouth, often due to stress, anxiety, or other psychological factors.
- Jaw deformities: When your upper jaw is narrow, the tongue will be in a lower position. This will prevent proper nasal breathing.
Mouth breathing effects:
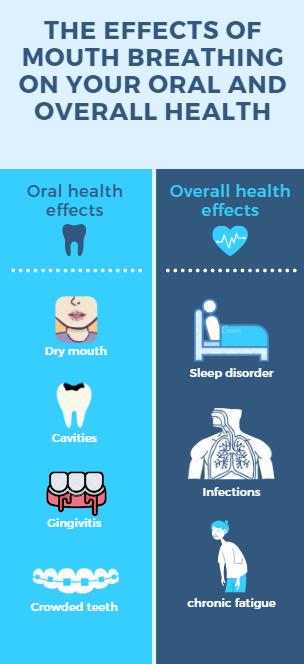
1. Effects on your oral health
One of the most common effects of mouth breathing is dry mouth. Saliva plays an important role in maintaining the oral microbiome and preventing oral disease. It benefits our oral health by:
- Protecting our teeth from bacteria and plaque by preventing them from attaching to the surface of the teeth;
- Reducing the number of harmful bacteria in our mouth;
- Protecting our gums;
- Regulating the acidity of the mouth.
As a result, people with dry mouths are more likely to develop cavities and gum disease.
2. Effects on your general health
1. Infections
The nose acts as a filter against viruses and particles in the air. When you breathe through your mouth, you may inhale antigens that can affect your airways.Mouth breathing and COVID-19
Studies have shown that nasal breathing can help reduce the viral load of SARS-CoV-2 and the symptoms of COVID-19 pneumonia by promoting more effective antiviral defense mechanisms in the airways. This is thanks to the nitric oxide that is naturally produced by the paranasal sinuses. It is known to have antimicrobial properties and allows a better oxygenation of the body.
2. Sleep disorder
Chronic mouth breathing can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to snoring, sleep apnea, and other sleep disorders. This can lead to fatigue, mood changes, and other health issues.3. Difficulty eating
People who breathe through their mouths have difficulty chewing food because they have to block their breathing during this time. This can affect the way they eat and cause digestive problems.4. Cognitive function:
Poor sleep quality due to mouth breathing and associated sleep disorders can affect cognitive function, including memory, attention, and problem-solving abilities.5. Facial growth:
Mouth breathers put their tongue in a low position. The upper jaw will then not be stimulated and will be narrower. Since the growth of the lower jaw is guided by the upper jaw, it will rotate downward and backward, resulting in a receding chin and a long, narrow face. This is also known as long-face syndrome.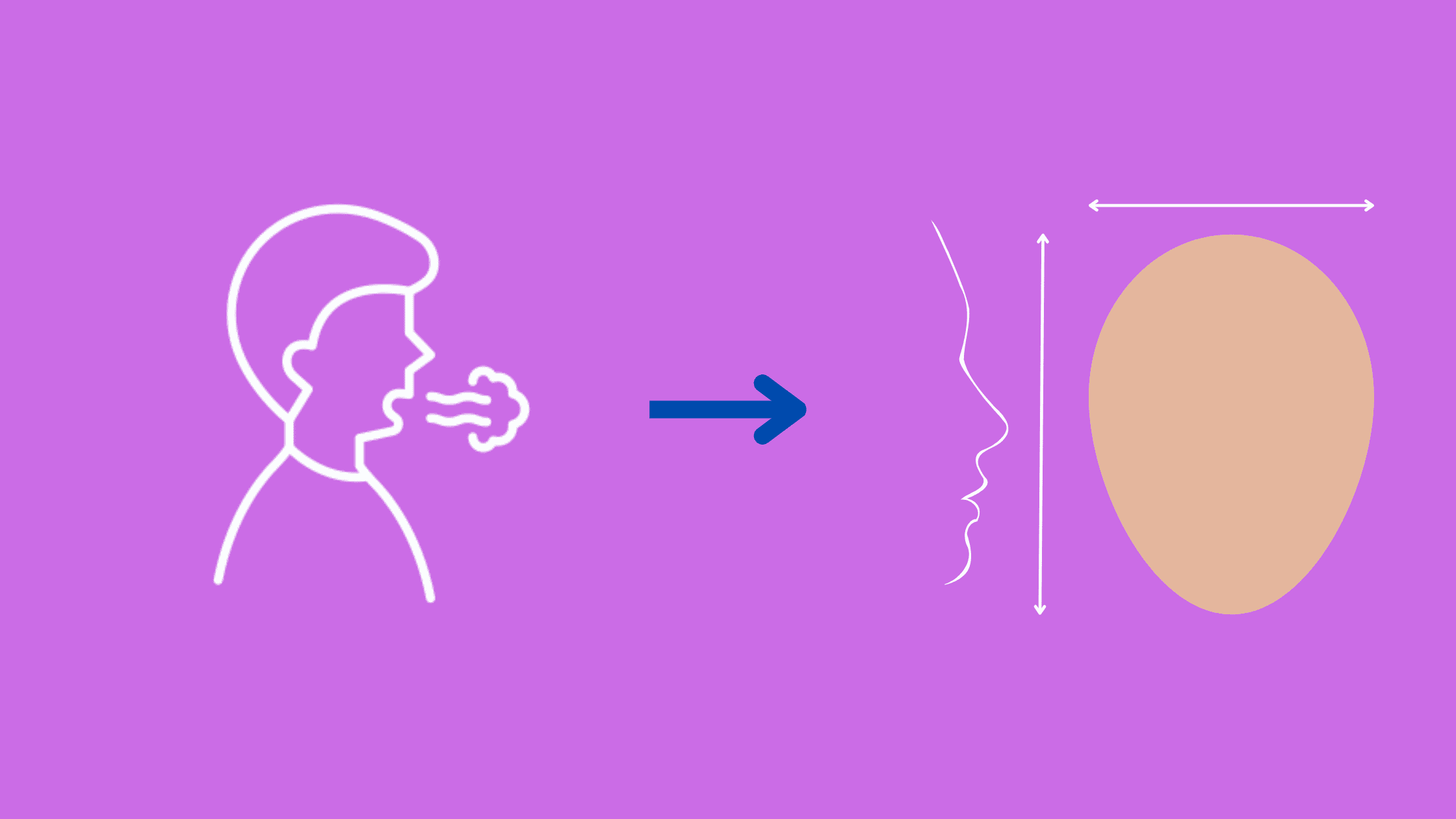
Why and how to treat mouth breathing?
Treating mouth breathing is important for several reasons, including improving oral and general health, enhancing sleep quality, and reducing the risk of associated health issues. This may involve different specialties, such as ENT, allergist, rehabilitation specialist, orthodontist, and maxillofacial surgeon.Here are some options that may be recommended to you to treat mouth breathing:
1. Addressing the underlying cause:
The first step in treating mouth breathing is to identify and address any underlying causes, such as allergies, sinusitis, or structural abnormalities.
Beforehand, you may need to treat an allergy or have surgery to remove the anatomical obstructions that prevent you from breathing through your nose.
Treating these conditions will help you alleviate mouth-breathing symptoms and return to a healthy breathing pattern.
2. Orthodontic treatment:
In the case of facial deformities, such as a too-narrow upper jaw, an orthodontic appliance such as a palate expander may be needed to stimulate jaw growth and widen the nasal cavity. This will also create enough space for the tongue to fit into the roof of the mouth, further contributing to nasal breathing.
However, if no growth potential is left, surgery may be the only remaining solution, particularly in severe cases.
3. Myofunctional therapy:
Myofunctional therapy involves targeted exercises to strengthen the face, mouth, and throat muscles. By engaging in these exercises, such as enhancing your breath and tongue posture, you can boost your nasal breathing quality and mitigate the adverse impacts of mouth breathing.
4. Lifestyle adjustments:
Making certain changes in your daily routine can ease mouth breathing symptoms. Here are a few examples:
- Stay aware of your breathing patterns and aim for nasal breathing whenever possible.
- Opt for nose breathing during workouts to encourage healthy breathing habits.
- Elevate your head slightly while sleeping to discourage mouth breathing during the night.
- Find strategies to reduce stress, as stress can contribute to mouth breathing tendencies.
- Develop the practice of keeping your mouth closed while at rest to promote better breathing through your nose.
- Could nasal nitric oxide help to mitigate the severity of COVID-19? https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7200356/
- Surgical approach of a vertical problem: the long face syndrome https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6587532/
- Guidelines proposal for clinical recognition of mouth breathing children https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4593528/
- Impact of airway dysfunction on dental health https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6986941/