Gum Pain Between Teeth: Potential Causes & Instant Relieve
 Oral pain, whether it’s in your teeth or gums, can be really annoying. It doesn’t just cause discomfort; it can also make simple daily activities like speaking and eating more difficult.
Oral pain, whether it’s in your teeth or gums, can be really annoying. It doesn’t just cause discomfort; it can also make simple daily activities like speaking and eating more difficult.
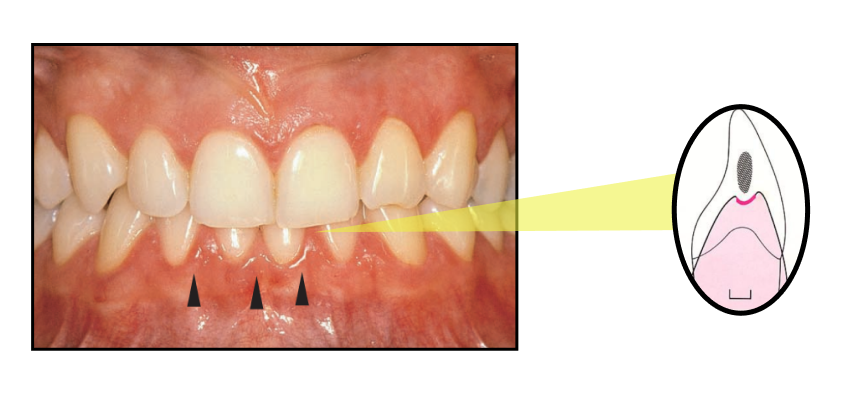
The gums between your teeth are actually the most delicate and fragile part of your gum tissue. They’re meant to be protected by your teeth, but once they’re exposed — even something as simple as food getting stuck there — can lead to significant discomfort and pain.
Improving your oral hygiene and cleaning the area properly is often enough to soothe the pain. However, if the pain doesn’t go away despite your best efforts, it’s important to see your dentist.
In this post, we’ll break down the most common causes of gum pain between teeth, the signs to watch for, and the most effective ways to get quick relief.
In this article...
1. Why the Gums Between Teeth Are More Sensitive
2. Most Common Causes of Pain Between the Gums
3. Ways to Get Instant Relief from Gum Pain
4. Takeaway
Why the Gums Between Teeth Are More Sensitive
The spaces between your teeth are tight and hard to keep clean, which is why they’re often the first spots to show signs of gum inflammation.
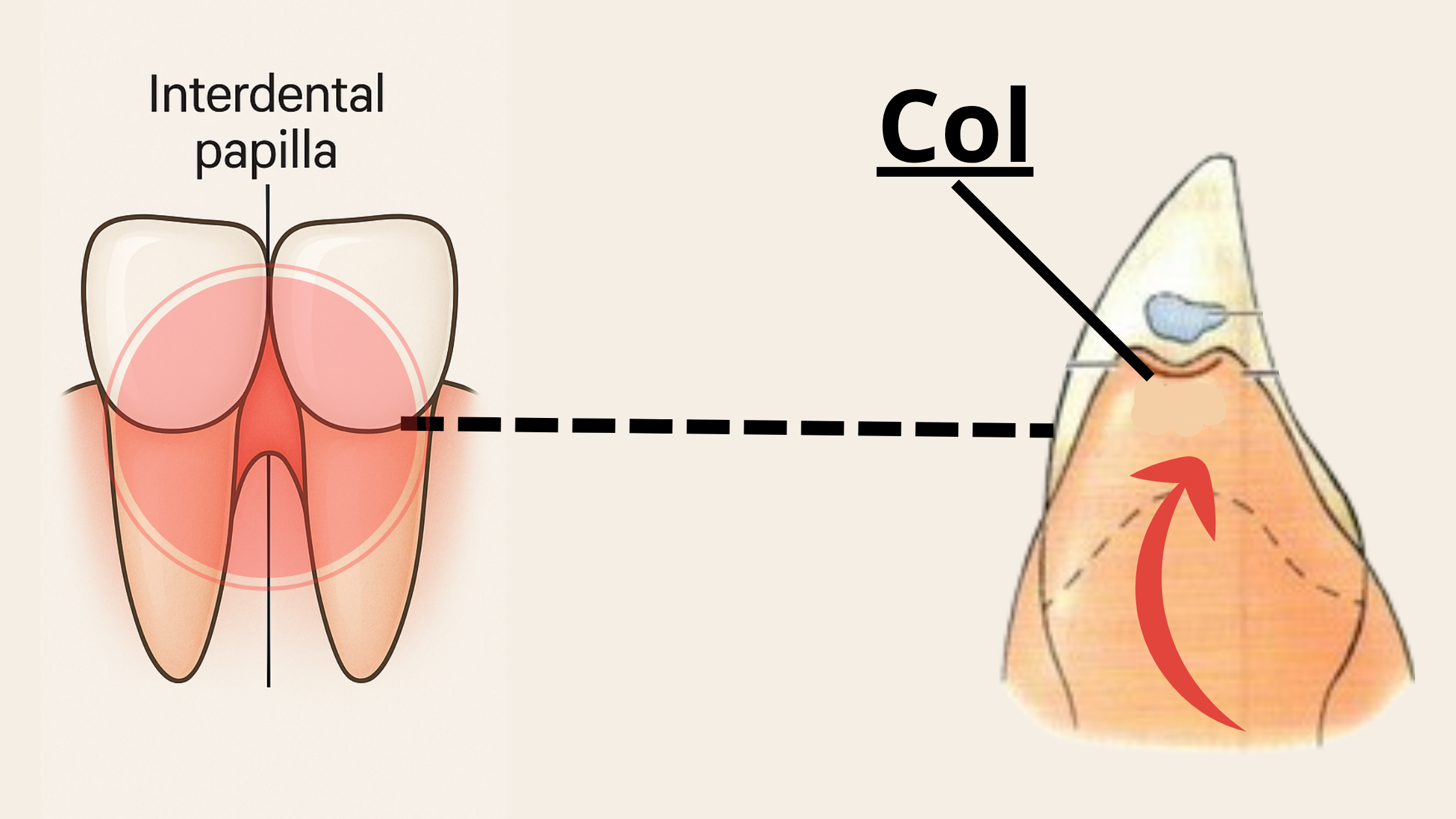
On top of that, the gum tissue in these areas—known as the col—is thinner and more delicate than the rest, making it easier to irritate or injure.
Even simple things, like pushing floss too deeply under the gum or having a piece of hard, crunchy food stuck between your teeth, can cause discomfort.
It's even worse if there are open gaps between your teeth, which can act like traps for food and plaque.
Most Common Causes of Pain Between the Gums (& How to Manage Them)
Many things can make the gums between your teeth hurt. Here are the most common reasons:1. Food Getting Trapped Between Your Teeth
If you don’t clean between your teeth regularly by flossing or using tools like interdental brushes or a water flosser, food and plaque can build up and get stuck. Over time, this can irritate your gums and lead to painful inflammation.
This is especially true if your teeth don’t touch each other firmly at proper contact points. These contact points act like protective umbrellas for the gums in between.
When your teeth no longer touch properly, they create gaps or open spaces where food can easily become trapped. This often happens after dental work, such as a filling or crown, that doesn’t fully restore the contact points. As a result, the gums between the teeth can become overstimulated, leading to symptoms like swelling, redness, bleeding, and pain.
Other common causes of gaps between teeth include receding gums, cavities, and misaligned teeth.
The pain often persists as long as food remains stuck. You may notice the pain getting worse during meals or right after eating.
When food buildup is the cause, you might also notice a bad taste in your mouth or bad breath. In more severe cases, the pain can even spread to your jaw or face.
How Do I Know If My Teeth Are Touching Properly?
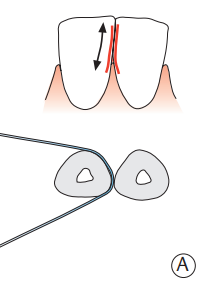 Your teeth’s contact points are healthy when you hear a small “click” as you gently pull dental floss down and out between your teeth. The surfaces should also feel smooth.
Your teeth’s contact points are healthy when you hear a small “click” as you gently pull dental floss down and out between your teeth. The surfaces should also feel smooth.
This clicking sound means the contact points between your teeth are tight and doing their job.
However, if your floss tears, won’t pass through the space, or slides in too easily because there’s a gap, it could mean your teeth aren’t touching the way they should.
Get Rid of Food Buildup
The solution is simply to clean the area to remove any debris. Here's what you can do:
- Floss gently, going slightly below the gum line to dislodge any food stuck there. If your gums are sensitive or you struggle with flossing, use a water flosser instead (it works better and can feel more comfortable).
- Brush your teeth gently using circular motions, and angle the bristles slightly toward the gum line. Always use a soft-bristled toothbrush and a gentle toothpaste.
- Once the area is clean, you’ll often notice instant relief.
- If the problem keeps coming back, see your dentist for a check-up. They may recommend a deep dental cleaning to remove plaque and tartar under your gum line. If the pain is caused by gaps between your teeth, your dentist may need to restore those spaces to keep food from getting trapped again.
2. Cavities
The tight spaces between your teeth are difficult to clean with a toothbrush alone, which makes them more likely to collect plaque. Over time, this can lead to decay and cavities.
The tricky part is that these spots are hidden from your sight. So, you might not even know you have a cavity between your teeth.
Early on, you may notice some sensitivity to sweet foods or hot and cold drinks. But if the cavity is left untreated, the decay can reach the tooth’s nerves. At that point, the pain can become much more intense. Even touching or pressing on the tooth might hurt.
How Are Cavities Treated?
Don’t delay treating a cavity — it won’t heal on its own, and waiting will only make it worse.
Here’s how cavities are usually treated:
- After numbing the area, your dentist will remove all the decayed and infected parts of the tooth.
- If the decay has reached the nerves, you may need a root canal. This procedure removes the damaged nerve tissue, then cleans, shapes, and fills the root canals.
- Depending on how much damage there is, your dentist may restore your tooth with either a filling or a crown.
3. Receding Gums
Receding gums happen when your gum tissue pulls away from your teeth, exposing the roots and making your teeth look longer than they used to be.
Because exposed roots are more sensitive, you may start to feel discomfort when eating or drinking hot, cold, or sour foods — or even when applying pressure while brushing.
On top of that, when the protective gum layer between your teeth breaks down, it leaves open spaces where food can easily get trapped. This can lead to more irritation, inflammation, and pain.
Treating Receding Gums
There are two main parts to treating receding gums:
- Stop the damage from getting worse by addressing the root cause.
- Cover the exposed roots and restore the gum line surgically.
If you notice your gums are starting to recede, here’s what you can do:
- Improve your oral hygiene: Switch to a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush and floss daily using the right technique. Simply improving your oral care routine can help stop further damage.
- Deep dental cleaning: If gum disease is behind your receding gums, you may need a professional deep dental cleaning to remove plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line.
- Gum grafting: For more severe cases, a gum grafting procedure may be needed to cover exposed roots, reduce tooth sensitivity, and protect the gums from further damage.
4. Gum Infection
If you notice signs like swelling, redness, bleeding, or intense, throbbing pain, you might have an infection that needs prompt treatment.
Here are some conditions, starting with the most common:
1. Gingivitis
Gingivitis, or gum inflammation, is the mildest and earliest stage of gum disease. It happens when plaque and bacteria build up along the gum line.
In its early stages, gingivitis might not cause any obvious symptoms, or the signs can be so mild you barely notice them. But as it progresses, it can lead to redness, swelling, tenderness, and gums that bleed easily.
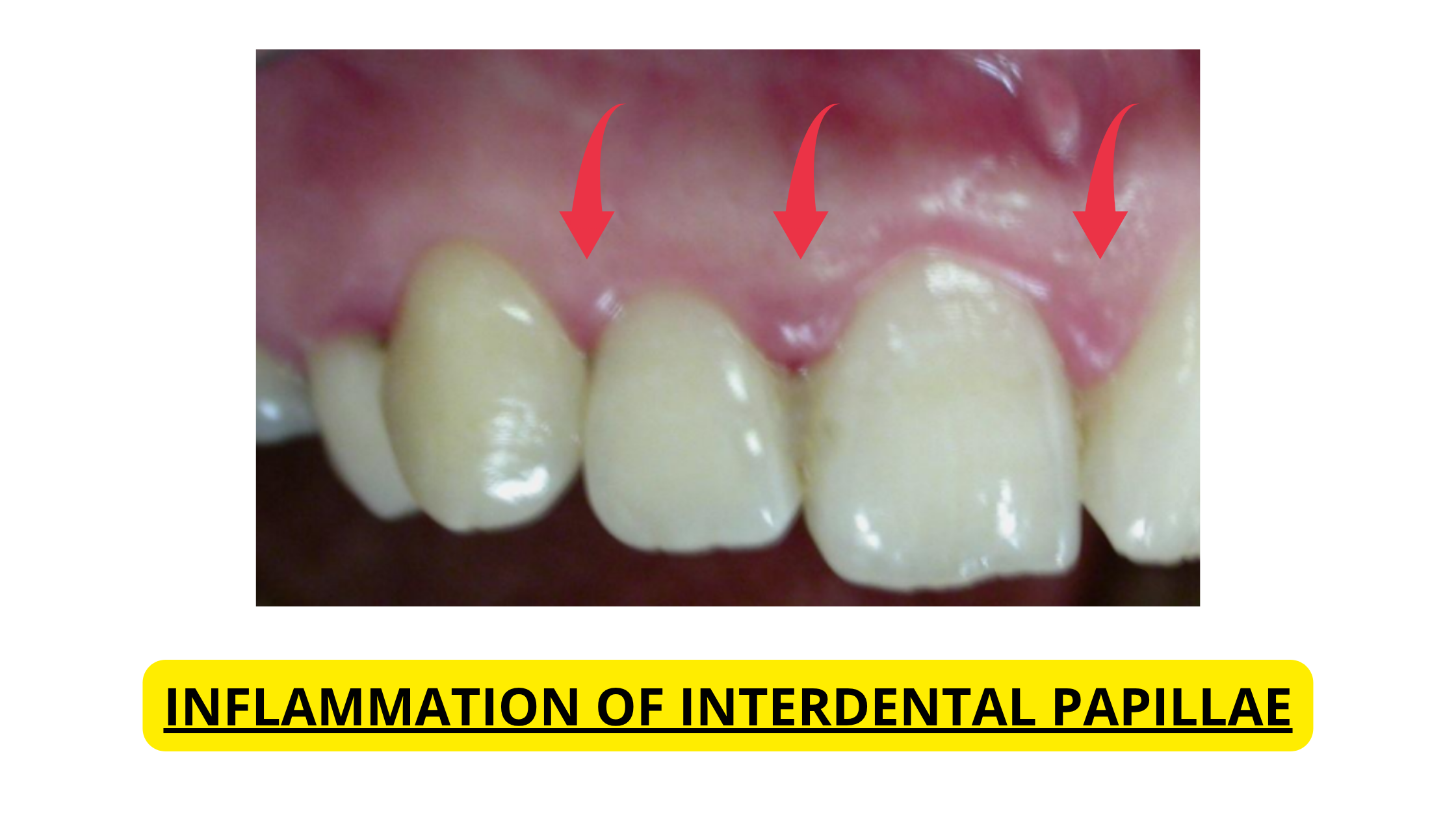
The good news? Gingivitis is completely reversible with good oral hygiene. Brushing and flossing daily, along with regular professional dental cleanings, can clear it up completely.
However, if left untreated, gingivitis can progress to more severe gum disease called periodontitis, which can cause more serious damage.
2. Gingival Abscess
A gingival abscess happens when a spot in your gums — usually near the gum line — becomes infected, leading to a buildup of pus and the formation of a small gum boil or pimple.
The most common cause is a piece of food, like a popcorn kernel, getting trapped under the gum line. But any foreign object — such as tartar, a toothpick, or even a fragment of a broken filling — can cause a gum abscess.
Typical signs of a gingival abscess include redness, intense pain, swelling, and sometimes a clear fluid that leaks from the gum. You might also notice a bad taste in your mouth, and in some cases, you could develop a headache or even a fever.
Treatment usually involves draining the abscess and removing the foreign object. Antibiotics aren’t always necessary, except if the infection has spread or is more severe.
3. Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis (ANUG)
ANUG is a rare but severe and extremely painful form of gum disease.
It causes rapid and widespread breakdown of gum tissue, leading to painful ulcers and areas of dead (necrotic) tissue that appear whitish or grayish, especially on the interdental papillae (the triangular gums between your teeth).
Other signs include intense pain, bleeding gums, bad breath, and sometimes a metallic taste in the mouth.
ANUG often develops when the immune system isn’t working properly. Stress, poor nutrition, smoking, and certain conditions like HIV infection can all be risk factors.
That’s why, if ANUG is diagnosed, your dentist or doctor may recommend blood tests to check for underlying health issues.
Treatment usually involves professional dental cleaning to remove dead tissue and bacteria, antibiotic therapy, and pain management. Because this condition is so aggressive, it’s important to get treatment as soon as possible.
Ways to Get Instant Relief from Gum Pain
Here are some tips that can help:- Dental Numbing Gel: Applying a dental numbing gel, such as Orajel, directly to the painful gum area can provide quick relief. Be sure to follow the directions on the label carefully.
- Saltwater Rinse: Rinse your mouth with warm salt water (dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water). Salt has excellent antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Clove Oil: Place a small amount of clove essential oil mixed with a carrier oil (like olive oil) onto the sore area. Clove oil has natural numbing and soothing effects.
- Apply a Cold Compress: Hold a cold compress near the painful area for a few minutes at a time. You can repeat this several times a day.
- Gently Brush and Clean Between Teeth: Keep up with good oral hygiene, but be gentle when brushing and flossing around the sore spot. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and a gentle toothpaste made for sensitive gums to avoid more irritation.
Takeaway
Gum pain is often caused by minor issues and can usually be relieved by simply cleaning the area well.However, if home treatments don’t help and the pain lasts more than a week, it’s important to book an appointment with your dentist to find out what’s really going on.
Persistent pain in your mouth should never be ignored — delaying treatment can only make the problem worse.