How to Stop Gum Bleeding at Home immediately (5 tips)
 If you notice your gums bleeding when you brush your teeth or chew something, you’re not alone.
If you notice your gums bleeding when you brush your teeth or chew something, you’re not alone.
Gum bleeding is a common issue, and it can sometimes look worse than it actually is. When blood mixes with saliva, it may seem like there’s a lot more than there really is.
In this article, we’ll break it down for you: the causes of gum bleeding, its different forms, how to stop it immediately at home, and when it’s time to see a dentist.
In this article:
1. The Most Common Cause of Bleeding Gums
2. Different Types of Gum Bleeding
3. How to Stop Gum Bleeding Immediately
4. Other Less Common Causes of Gum Bleeding
5. When Should You See Your Dentist?
The Most Common Cause of Bleeding Gums
There are many reasons why your gums might bleed, but the most common cause is gum disease—specifically, inflammation. Gum inflammation is a common condition that affects almost everyone to some degree.When you skip flossing or don’t brush properly, bacteria build up in your mouth, forming plaque on your teeth and along the gum line. Over time, these bacteria can creep below your gumline, triggering inflammation. The result? Your gums become puffy, sore, red—and they may start to bleed.
But bleeding gums aren’t a disease on their own; they’re just a symptom of gum disease. To stop the bleeding, you need to address the root cause.
Different Types of Gum Bleeding
How and when your gums bleed can vary depending on the severity of inflammation.In mild cases, bleeding may only happen occasionally—like when you brush your teeth or bite into something hard.
In more advanced gum disease, your gums may start bleeding on their own, even without any contact. If this occurs, it’s important to see your dentist, as it’s a sign of severe inflammation. You may also have tartar (hardened plaque) that cannot be removed at home.
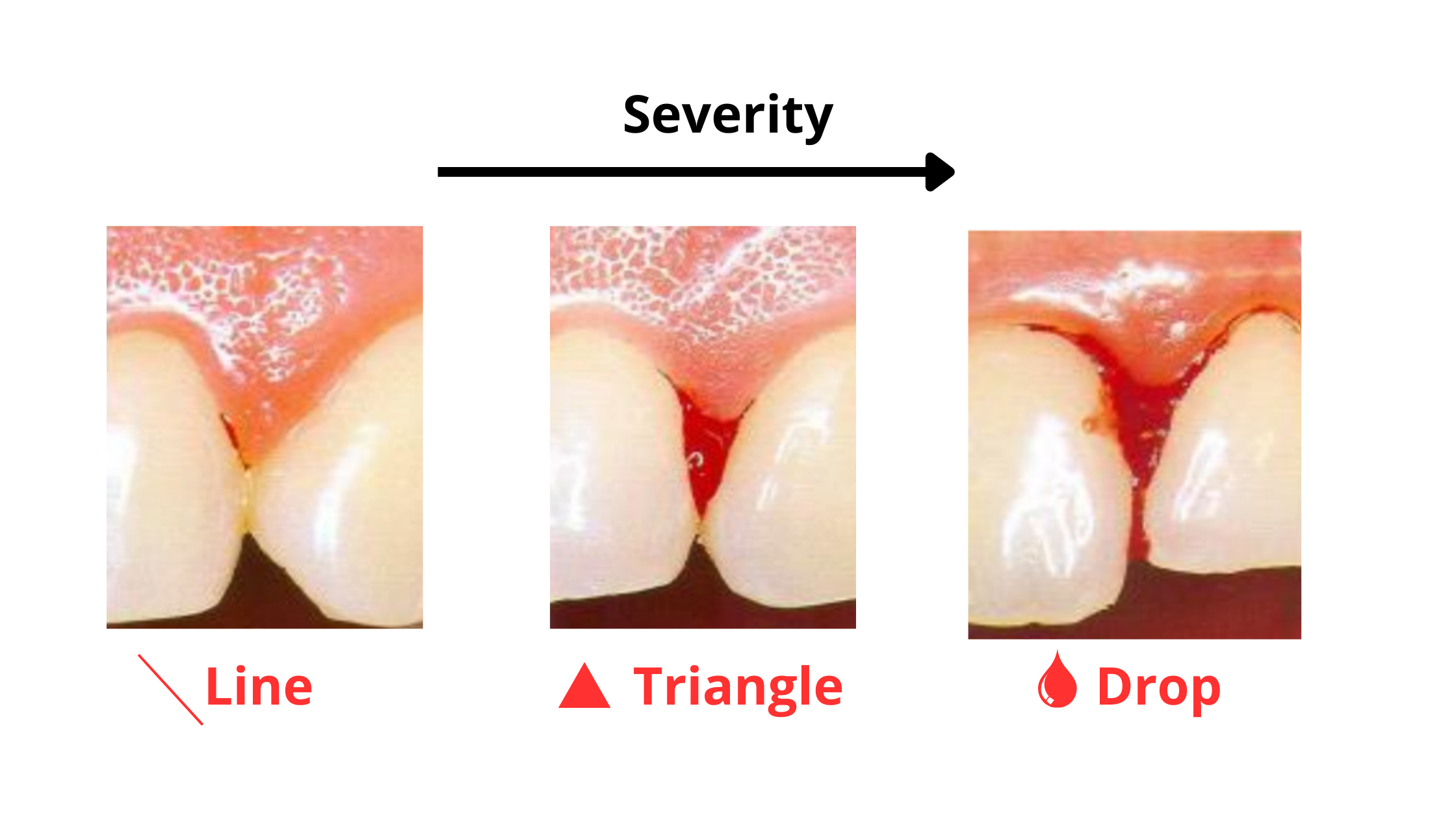
The amount of bleeding can also vary. It may appear as a small dot or thin line along the gum line, or in more severe cases, it can form drops.
How to Stop Gum Bleeding Immediately
Here are simple steps you can take at home to stop gum bleeding immediately.1. Brush and Floss Properly
The first and most important step is to brush and floss correctly. This helps remove plaque, the main culprit behind inflammation and gum disease.
- Use gentle, circular motions to brush your teeth and along the gumline. Use the Modified Bass Technique.
- Floss between your teeth, making sure to slide the floss slightly under the gumline.
The areas between your teeth are the perfect spots for bacteria and plaque buildup as they are well hidden from the brushing action. For that reason, they are the most common sites of gum inflammation.
You may notice more bleeding when you start cleaning your teeth properly, but this is completely normal. Stick to your routine, and within a week or two, your gums should heal, and the bleeding will stop.
2. Apply Firm Pressure to the Bleeding Spot
If the bleeding doesn’t stop, try applying firm pressure to the affected area with a cotton roll or a damp tea bag (not herbal tea).
Tea contains tannins, a natural compound with an astringent effect that helps shrink blood vessels and slow down bleeding. Hold it in place for a few minutes for the best results.
3. Saltwater Rinse
Rinsing with salt water several times a day can help control bleeding and soothe inflamed gums. Mix ½ teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and swish it around your mouth for about 30 seconds before spitting it out.
Saltwater not only reduces bacteria and plaque but also has an astringent effect.
4. Complement Your Oral Hygiene with Mouthwash
You can use an antibacterial mouthwash alongside brushing and flossing to help eliminate any remaining harmful bacteria in your mouth.
However, mouthwash is never a stand-alone treatment. It should always complement daily brushing and flossing, not replace them.
Bacteria living in plaque can be up to 1,000 times more resistant to antibacterial products, which is why plaque must be disrupted first through brushing and flossing before using mouthwash.
There are many options available; some recommended brands include Parodontax and Listerine.
5. Make Your Own Natural Mouthwash
You can make your own mouthwash using essential oils. Studies have shown that essential oil-based mouthwashes can be just as effective as antibacterial mouthwashes in reducing gum inflammation.
Here’s how to do it:
- Choose an essential oil – Tea tree, clove, or peppermint oil are great options, as they have strong anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.
- Dilute it properly – Mix 3 drops of essential oil with 1 tablespoon of carrier oil (such as coconut or sesame oil).
- Swish the mixture – Rinse it around your gums for at least 5 minutes to let it work.
- Spit it out – Do not swallow the oil. After spitting, brush your teeth as usual.
Other Less Common Causes of Gum Bleeding
While gum disease is the most common cause, some less frequent conditions can also lead to gum bleeding. These are usually related to disorders that affect the body's ability to form blood clots (hemostasis), such as hemophilia, anemia, or Von Willebrand’s disease.People taking blood-thinning medications like warfarin, heparin, or aspirin are at a higher risk of gum bleeding, as these drugs reduce the blood’s ability to clot.
Other, less common forms of gum inflammation that aren’t caused by plaque include:
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy
- Viral or fungal infections
- Allergies
- Autoimmune diseases
When Should You See Your Dentist?
You should visit your dentist if:- The bleeding is heavy and difficult to control.
- It persists for more than two weeks despite proper oral care.
Chronic or excessive bleeding is often a sign of advanced gum disease, which requires professional treatment. Your dentist may recommend scaling and root planing to remove plaque and tartar buildup and may also prescribe a specialized mouthwash to help manage the infection.
If your bleeding is caused by a systemic condition (such as a clotting disorder), treatment may involve supplementing the missing clotting factor.