4 Common Things That Happen When Gums Start to Recede
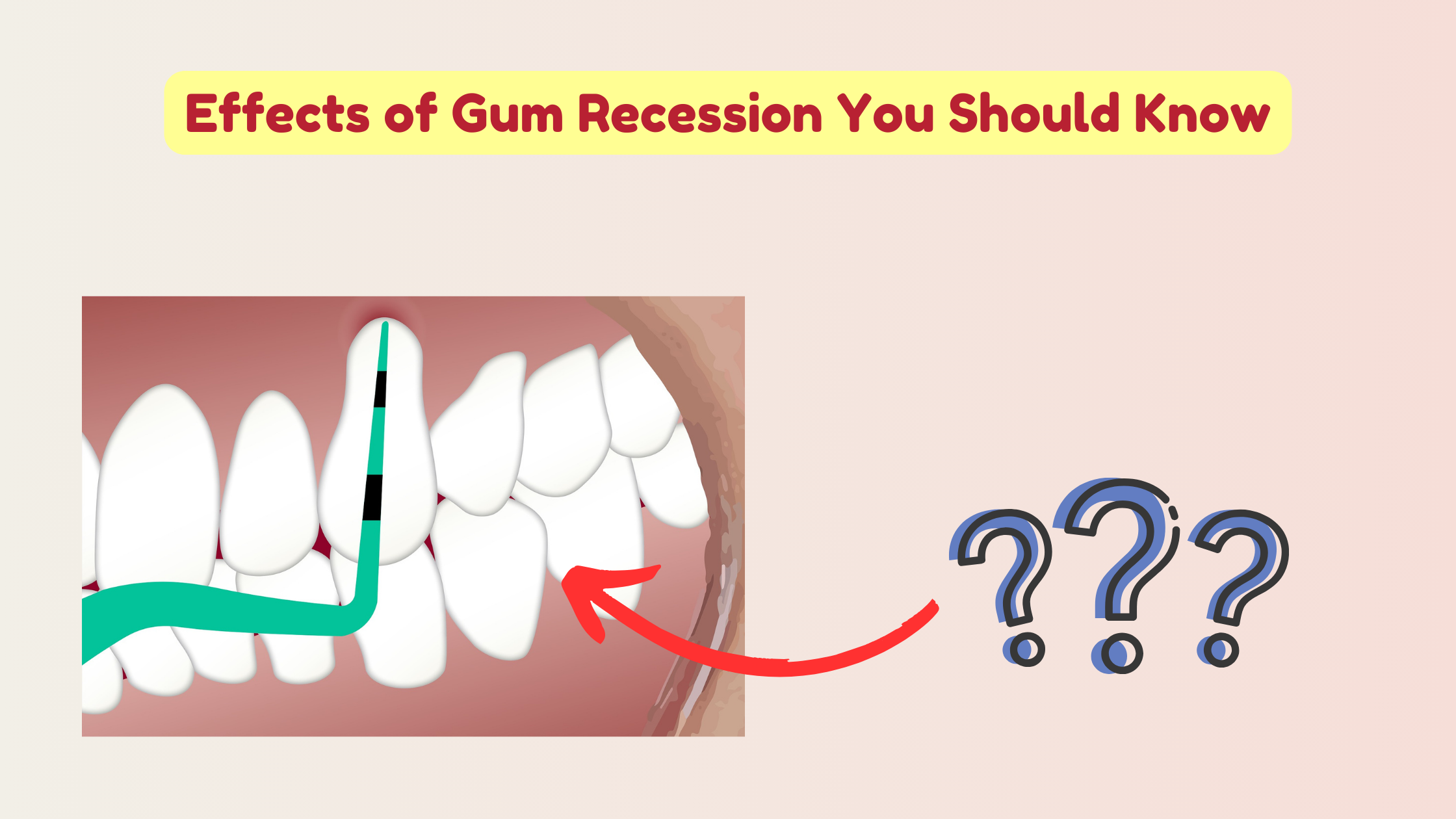 Have you ever wondered what happens to your mouth when your gums start to recede?
Have you ever wondered what happens to your mouth when your gums start to recede?
Gum recession is a common dental issue that can affect anyone, though it’s more common among adults and the elderly. It’s not just a cosmetic concern—it can have a significant impact on both your oral health and overall well-being.
In this post, we’ll explore 4 things that are more likely to occur when your gums begin to recede.
In this article:
1. Root Decay and Wear
2. Dental Sensitivity
3. Longer Teeth
4. Loose Teeth
5. Stop the Damage and Heal Your Gums Before It’s Too Late
1. Root Decay and Wear
According to a CDC report, tooth decay is the most common health condition worldwide, affecting nearly 90% of adults aged 20 to 64.Decay can occur on any part of a tooth—between teeth, on chewing surfaces, or along the front and back. However, it’s less likely to start on the roots simply because they are normally covered and protected by healthy gums.
Once gums recede, this natural protection is lost. The roots are weaker and not designed to withstand the acidic environment of the mouth. When exposed, they become much more prone to decay and wear.

The tricky part is that root surfaces naturally have a rough texture, which traps plaque and makes cleaning more difficult. Worse still, decay and wear on the roots progress about twice as fast as they do on the visible top part of the tooth.
If left untreated, the damage can quickly reach the tooth’s nerve, leading to severe complications such as infections and tooth loss.
That’s why people with receding gums need to take extra care with their oral hygiene.
2. Dental Sensitivity
When the roots become exposed, another common issue is sensitivity.Unlike the crown of the tooth, roots are not covered by the strong protective enamel. They’re made of dentin, which is porous and contains tiny channels called tubules. These tubules are directly connected to the nerves inside the tooth.
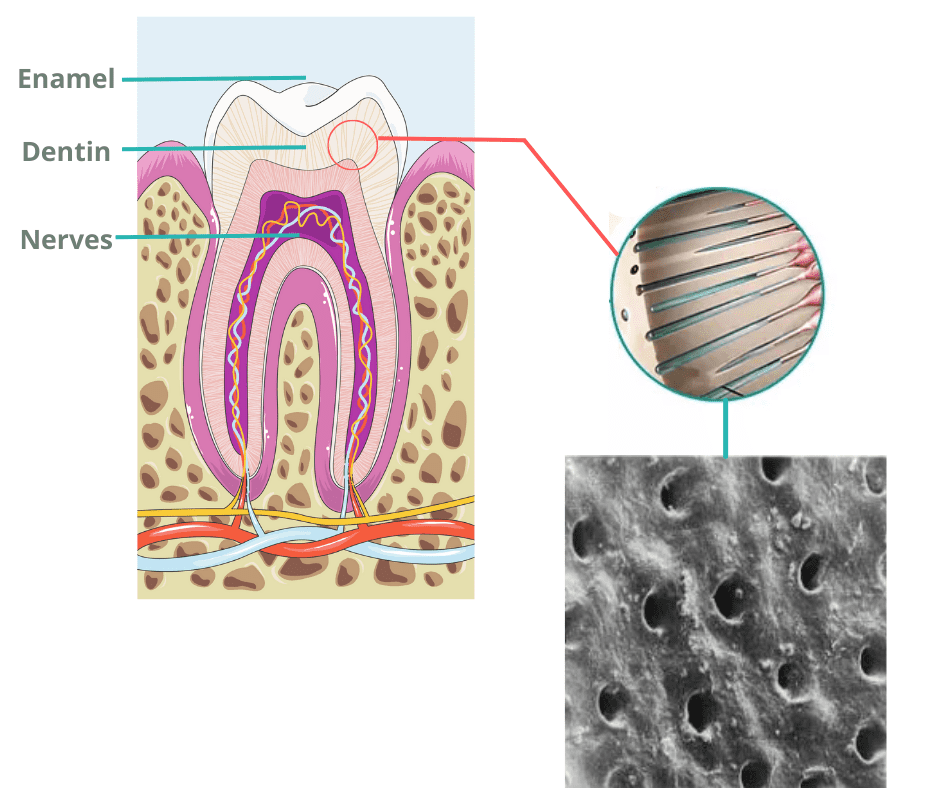
When gums recede, anything you consume—cold, hot, sour, or sweet—can travel through these channels and stimulate the nerves, triggering sharp, brief pain.
This sensitivity can make even simple activities, like eating or breathing through your mouth, uncomfortable.
3. Longer Teeth
What gives teeth a healthy, attractive look is an even gum line that hugs them firmly. But when gums recede and roots become exposed, teeth can start to look unusually long.
Another common concern is the appearance of black triangles—small dark gaps between the teeth that form when the gum tissue that once filled those spaces pulls back.
These cosmetic issues are one of the main reasons patients seek treatment. They can affect the way your smile looks and often take a toll on self-confidence.
Gum recession isn’t just a dental issue—it’s a condition that can affect both your appearance and your overall quality of life.
4. Loose Teeth
In most cases, gum recession doesn’t happen on its own—it’s usually linked to bone loss.This is especially true in advanced gum disease, where bacteria and chronic inflammation are involved.
When brushing and flossing are neglected, plaque builds up along the gumline. Over time, the harmful bacteria can penetrate deeper into the gums, attacking the bone and ligaments that support your teeth.
That’s when chronic inflammation kicks in, and over time, it can do more harm than good.
If left untreated, the support system of your teeth breaks down. Your teeth may begin to shift, loosen, or, in severe cases, fall out completely.
Stop the Damage and Heal Your Gums Before It’s Too Late
The most effective way to deal with receding gums is to act early—before the problem gets worse and becomes much harder to treat.The first step is to tackle the root cause, which usually falls into one of two categories: plaque-induced gum disease and trauma (chronic irritation).
- Plaque: A sticky, whitish film packed with bacteria—and the main culprit behind cavities and gum disease.
- Trauma: Persistent irritation—like aggressive brushing or using a hard-bristled toothbrush—can gradually damage and wear away your gums over time.
Stop gum disease:
If gum disease is the cause, the only way to stop further damage is to see your dentist for a professional cleaning.
This procedure, also called scaling and root planing, is the standard treatment for most cases of gum disease. Its goal is to thoroughly clean your teeth and remove plaque and tartar from both above and deep below the gum line.
Advanced gum disease—when the bone and gums are pulling away—can’t be treated at home, and it won’t heal on its own.
The longer treatment is delayed, the more the disease progresses, the more damage it causes, and the harder it becomes to treat.
Stop gum trauma:
If chronic irritation or trauma is the real cause, all you need to do to stop receding gums from progressing is remove the source of the trauma. Here are some tips:
- Brush gently using circular motions.
- Avoid horizontal strokes, as they can be more damaging to your teeth and gums.
- Make sure to brush all surfaces of your teeth, including along the gum line, to help stimulate blood flow.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush or, ideally, an electric toothbrush with a pressure sensor that alerts you when you're applying too much pressure.
- If you grind or clench your teeth, ask your dentist for a mouthguard to protect your teeth and gums.